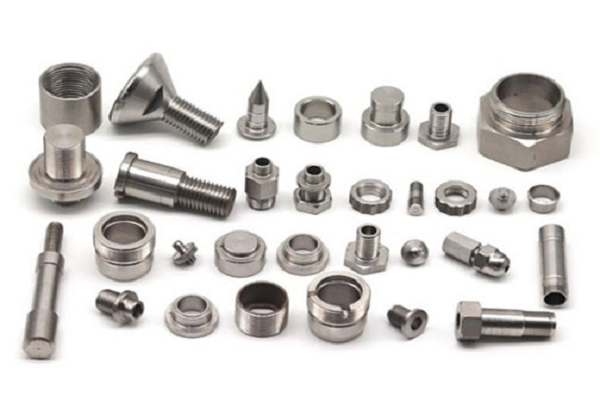
Forging Parts
Forging parts is a vital manufacturing process that transforms metals into high-performance components by applying heat and mechanical force. This technique results in stronger, more durable materials compared to traditional casting. It is integral to industries like aerospace, automotive, construction, and energy, where strength and reliability are paramount.
The Forging Process and Techniques
The forging process involves heating metal until it becomes malleable, then shaping it using mechanical force. There are several forging methods, each suited to different types of components:
- Open Die Forging: Used for large, heavy-duty parts such as shafts and structural components, open die forging is ideal for producing robust parts that can handle extreme stress.
- Closed Die Forging: This method is perfect for high-precision, smaller components like automotive parts, where tight tolerances and complex shapes are required.
- Impression Die Forging: A refined version of closed die forging, impression die forging ensures minimal material waste while achieving highly intricate shapes and designs.
These techniques offer enhanced strength, fatigue resistance, and superior mechanical properties compared to cast or welded parts.
Historical Evolution of Forging
Metal forging has a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations. The Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans used rudimentary tools to forge weapons, tools, and decorative items. The Industrial Revolution marked a turning point in the forging industry, with the introduction of hydraulic presses and mechanical hammers that significantly improved production speed and efficiency. Pioneers like Henry Ford integrated forging into the automotive industry, revolutionizing mass production.
Modern Applications of Forging Parts
Today, forged parts play a crucial role across several high-performance industries:
- Aerospace: Forged aerospace components like turbine blades, structural parts, and fasteners are essential for aircraft safety and efficiency. Titanium and aluminum forgings are particularly valuable due to their light weight and high strength.
- Automotive: The automotive sector relies heavily on forged automotive parts, such as crankshafts, pistons, and suspension components. These parts offer unmatched strength and performance under high stress and harsh conditions.
- Energy: The oil and gas industry depends on forged steel components like valves and pumps, which must endure extreme pressures and temperatures. Forging ensures reliability and longevity in high-stakes environments.
- Construction & Heavy Machinery: Forged steel components are indispensable in heavy machinery. Parts like gears, axles, and shafts undergo extreme wear and stress, making forged steel parts the preferred choice for durability.
Technological Advancements in Forging
Recent technological innovations have transformed the forging process. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software allow engineers to design optimized parts, ensuring minimal waste and maximum material efficiency. Additionally, 3D printing has introduced hybrid manufacturing methods, combining traditional forging with additive techniques to create complex geometries.
The development of advanced materials like nickel-based superalloys and high-strength titanium alloys has expanded the range of applications for forged components, especially in industries that demand materials that can withstand high temperatures and stresses.
Sustainability in Forging
The forging industry has also made strides toward sustainability. Traditional forging requires significant energy, but there is growing focus on green manufacturing practices. By adopting energy-efficient methods and recycling scrap metal, manufacturers are reducing their environmental impact. Using recycled materials in the forging process helps conserve resources and lower production costs, contributing to a more sustainable future for the industry.
The Future of Forging Parts
Looking ahead, the demand for custom forged parts is expected to grow, especially with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy technologies. As these sectors expand, there will be a need for lightweight yet strong forged components. Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) will also drive the future of forging, improving manufacturing efficiency, precision, and safety. Smart factories equipped with IoT sensors will enable real-time monitoring and control of forging processes.
Why Choose Forged Parts?
- Strength and Durability: Forged components offer superior mechanical properties, making them ideal for high-stress, high-performance applications.
- Precision and Customization: Custom forged parts are tailored to meet specific industry needs, ensuring a perfect fit for unique requirements.
- Sustainability: By using recycled metals and adopting energy-efficient practices, the forging industry is moving towards more sustainable production methods.
- Cost Efficiency: While initial costs may be higher, the longevity and performance of forged parts provide significant long-term savings.
REQUEST A QUOTE